RATIO:
Ratio measures change
in “X” per unit change in”y”.
Ratio = x/y
There are different types of ratio:
i)
When we have numerator and denominator belongs
to the same population.
ii)
When we have numerator and denominator belongs
to the different population (universe). We call the ratio as proportion (specific
name of ratio).
Proportion= x/x+y
Proportion tends is equal to zero if x=0 and proportion is equal
to 1 if y=0.
Ratio indicates the relative magnitude of a numerator and denominator.
SEX RATIO:
Sex ratio is defined as
the male population and female population presenting in percentages. As:
R= Male/Female
* 100
Sex ratio means male per 100 female. We can calculate different types of
sex ratio.
Sex ratio of birth:
Number of males’ birth per 100
female births. Ratio if less than 100 means more female than male birth. If
ratio=100 same number of male and female birth. If the ratio is greater than
100 means more males than females. In human population there is more male birth
then female birth with ratio generally between 104 and 107.
CHILD WOMEN RATIO:
Demographers define some age group and gave different name.
i)
ADULT: Zero years, for purpose of
classification all babies who have not reached their first birth date.
ii)
CHILD: All those children who have not
reach their fifth birth date (0-4) years.
iii)
YOUTH: All those children who have not
reach their 15 birthday (5-14) years.
iv)
YOUNG: Adults and economically active
working(15-60)
v)
OLD AGE OR AGED: Age includes from 60+.
If proportion of old age population start increasing then this type of population
is called ageing population.
DEPENDENCY RATIO:
Dependency ratio is
observed as;
LABOR FORCE
PARTICIPATION:
It
is not calculated for entire world but for small segment:
TERRITORIAL
DISTRIBUTION RATIO:
It is defined as the ratio between populations in a segment of territory
to the total population of the country. For example;
DENSITY OF POPULATION:
It is the ratio between total populations to the total area to which the
population belongs, for example:
It shows how densely an area is populated. A low value indicates
sparsely populated area.
RATES:
Rate measures the frequency with which an event occurs in a define
population during a given length of time. Rates are special cases of a ratio.
Rates are associated with population changes. Numerator counts of events that
occur during a period. Denominator is a mid point population or person years or
other person time unit of exposure for the same period at the numerator.
TOTAL FERTILITY RATE:
ASFR through gives an
indication of fertility behavior in a very logical manner, however, it requires
a grasp of about 7 values. Hence to abbreviate and to arrive at a one single
index ASFR are summed and multiplied by size of age groups of mother (k) to
yield Total Fertility Rate (TFR).
GROSS REPRODUCTION
RATE:
A mother (female) is going to be replaced by female in future,
therefore, as an index of replacement we must calculate an index taking female
birth only. Hence multiplying the TFR by the ratio of female birth with total
births, yielding a new index known as Gross Reproduction Rate (GRR)
Where F: ratio of female births.
NET REPRODUCTION RATE:
However all female born will not survive to reach the age of their
mothers, hence a further refinement in GRR is made by multiplying it by the
proportion of survival si, the resultant is known as Net
Reproduction Rate (NRR).
Where si: survival proportion
of female and birth to age of their mothers. This can be found from lx
column of life table si = li/l0.
Generally TFR > GRR > NRR and the ratio
between them is around 50%.
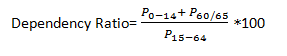






Your blog is very informative and I am here with the simple and exact definition of ratios and proportion,The ratio is said to be a comparison between two similar quantities that is obtained by dividing one quantity with the other and they are represented by : symbol and proportion is a statement which shows the equality of two ratios.
ReplyDeleteThank you for the valuable information :)
Delete